A Feasibility-Driven Approach to Control-Limited DDP
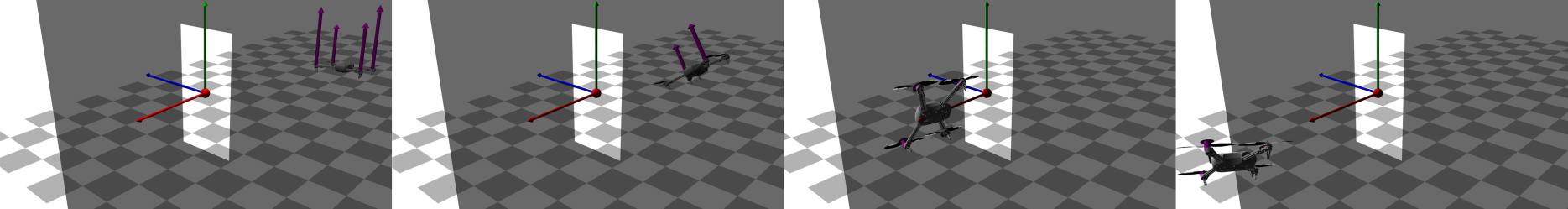
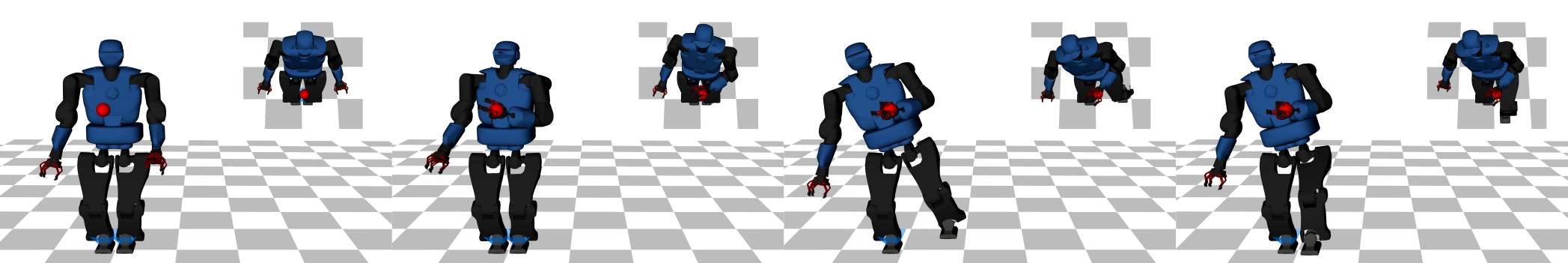
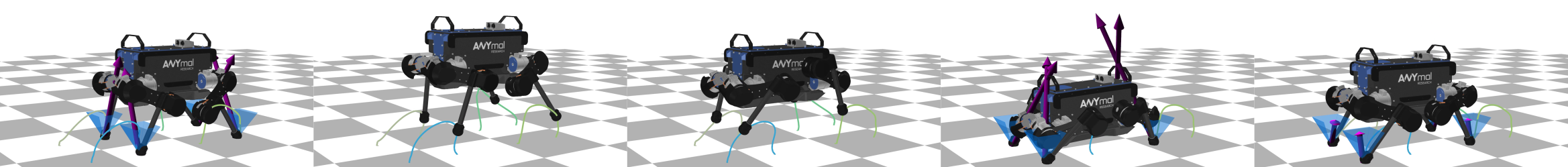
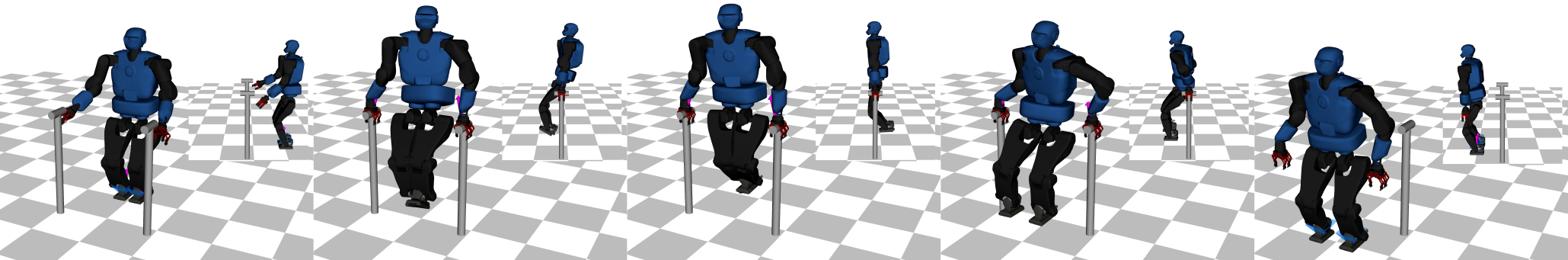
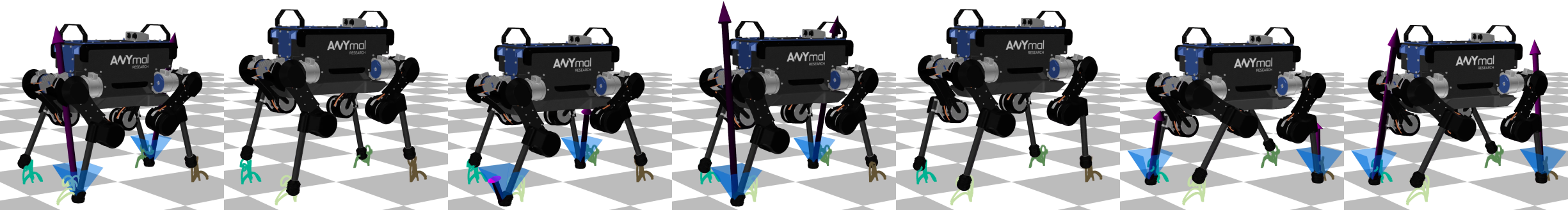
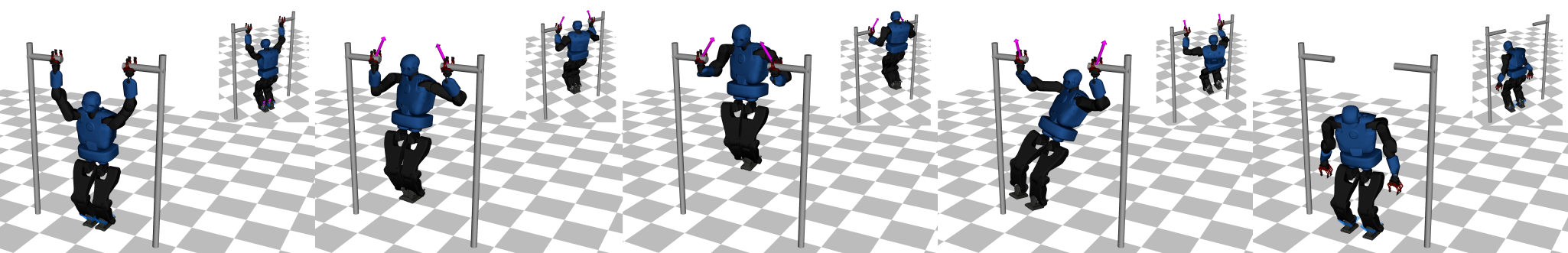
Differential dynamic programming (DDP) is a direct single shooting method for trajectory optimization. Its efficiency derives from the exploitation of temporal structure (inherent to optimal control problems) and explicit roll-out/integration of the system dynamics. However, it suffers from numerical instability and, when compared to direct multiple shooting methods, it has limited initialization options (allows initialization of controls, but not of states) and lacks proper handling of control constraints. In this work, we tackle these issues with a feasibility-driven approach that regulates the dynamic feasibility during the numerical optimization and ensures control limits. Our feasibility search emulates the numerical resolution of a direct multiple shooting problem with only dynamics constraints. We show that our approach (named BOX-FDDP) has better numerical convergence than BOX-DDP+ (a single shooting method), and that its convergence rate and runtime performance are competitive with state-of-the-art direct transcription formulations solved using the interior point and active set algorithms available in KNITRO. We further show that BOX-FDDP decreases the dynamic feasibility error monotonically—as in state-of-the-art nonlinear programming algorithms. We demonstrate the benefits of our approach by generating complex and athletic motions for quadruped and humanoid robots. Finally, we highlight that BOX-FDDP is suitable for model predictive control in legged robots.

